Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD)
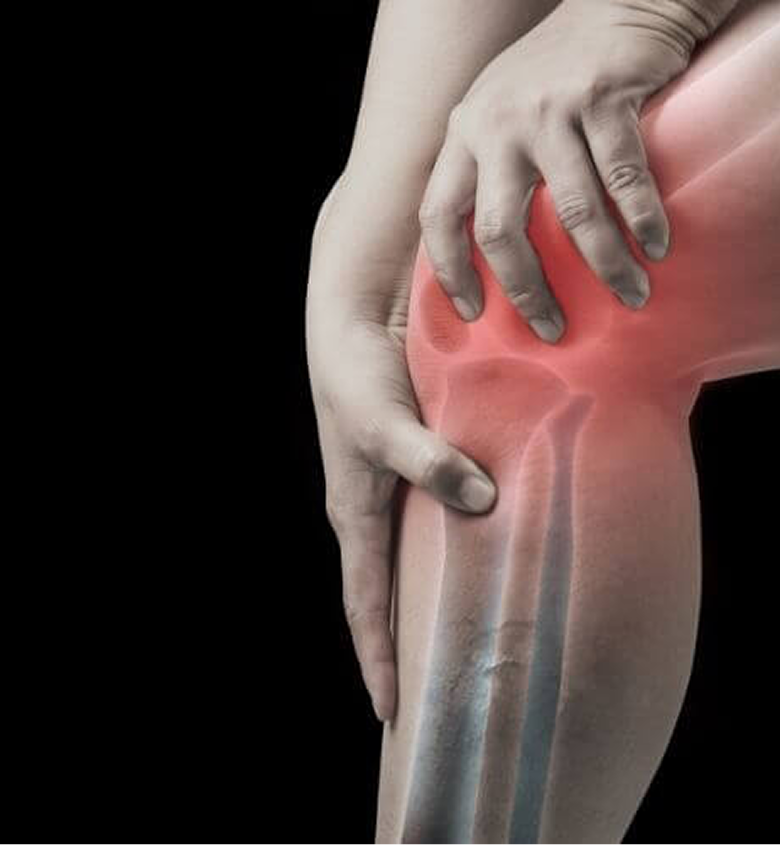
Osteochondritis Dissecans or OCD of the knee is a condition that affects the joint where your thigh bone and shin bone meet. In this condition a small piece of bone and the cartilage that covers it begin to loosen because they are not receiving enough blood supply. When this happens the bone and cartilage can become unstable which leads to pain swelling and stiffness in the knee.
If the condition is not treated the loose piece can break free and cause long-term damage to the joint surface. This may make it harder to stay active and can increase the risk of arthritis later in life. OCD most often appears in children and teenagers who are very active in sports but adults can develop it as well. Early diagnosis and proper care are important because treatment options can range from rest and physical therapy to surgery depending on how severe the problem is.

While the exact cause isn’t fully understood, several factors may contribute:
OCD symptoms can vary, but common signs include:
Doctors use a combination of approaches to diagnose OCD:
Treatment depends on the patient’s age, the stability of the lesion, and how advanced the condition is:
Learn about the doctors and centers dedicated to advancing Knee OCD care worldwide.
Get clear information on what it is, who it affects, and how it’s diagnosed.
Explore physical therapy routines and strategies that support healing and long-term joint health.
Access educational articles, guides, and tools designed to help you and your family navigate care.